Simple Scrabble
Introduction
Scrabble is a game where players get a set, or "hand", of wooden pieces, each one with a letter and point value on it. On their turn the player forms a word using some of the letters from their hand and places them on the board. The board has places for the wooden pieces, marked with special symbols, some of which will have a "multiplier" effect on the letter point value that is played in that location. In the real Scrabble, the board is a large square and letters must be played in such a way that each word connects to the others that have been played similar to a crossword puzzle. In our simpler version of Scrabble, the board is just a single horizontal strip and a player plays by inserting a word on the strip beginning anywhere on the strip as long as the word will fit and as long as they have the letters in their hand to play.
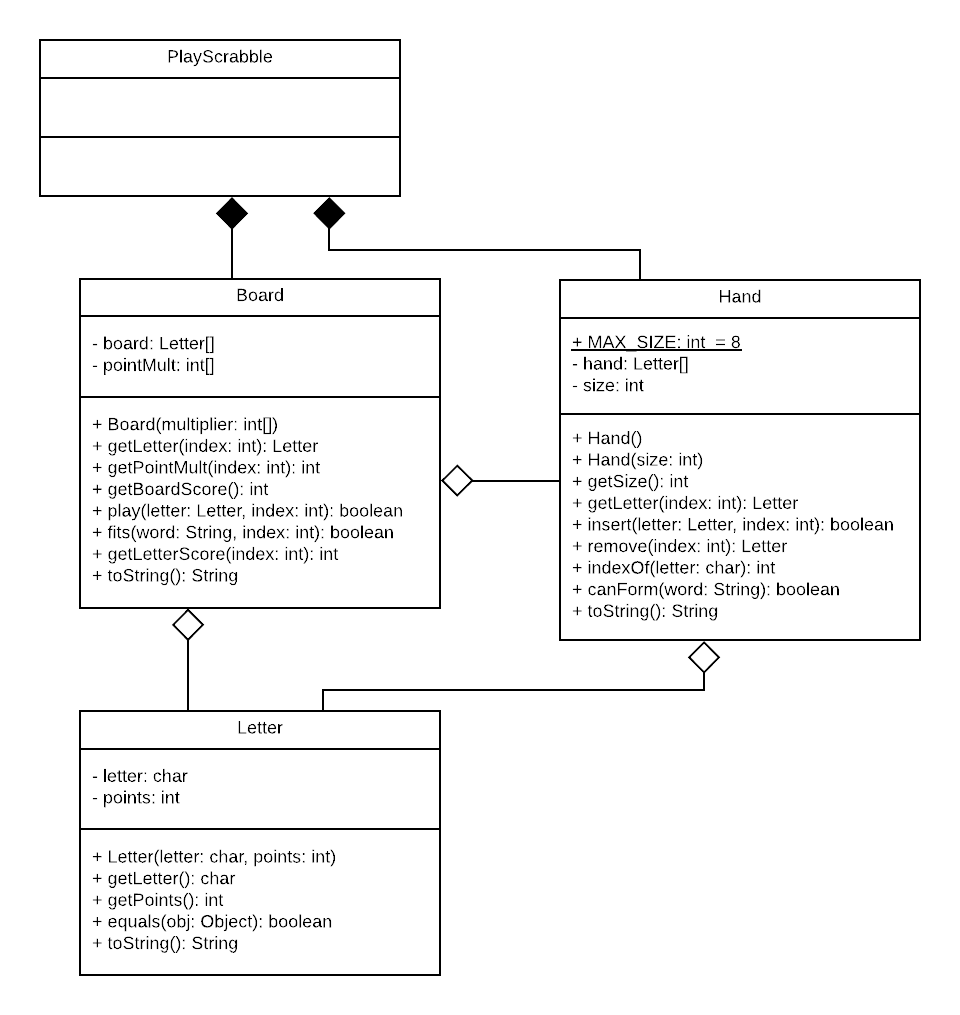
You must implement the three classes,
Letter.java, Hand.java, and Board.java from the UML
diagram below. The other classes shown, PlayScrabble.java and individual test classes for each of the classes you must
implement are provided for you. These are the same tests used by Autolab so you should not need to submit to Autolab until you are finished.
For this assignment, you will be limited to 5 submissions on Autolab.
Submission and Honor Code
Submissions should be made by the due dates listed on Canvas. There are no late submissions unless specified by your instructor otherwise. The Autolab results will reflect the no late submissions policy. Only the latest submission to Autolab will be graded and code that does not compile will receive a 0, so please be careful with last minute submissions. Your final grade will be determined largely by correctness as determined by your Autolab score, but documentation, and overall code quality will also be considered.
Though you are encouraged to discuss concepts with peers, teaching assistants and the instructor, the source code you submit should be your own work and something you could replicate on your own. Representing someone else's work as your own, in any form, constitutes an honor code violation. Directly copying or using the same code is an honor code violation. It is also a violation of the honor code to "render unauthorized assistance to another student by knowingly permitting him or her to copy all or a portion of an examination or any work to be submitted for academic credit." That means that you can be written up for an Honor code violation if you share your code with someone else, even if you wrote it completely on your own. If you violate the University Honor Code, you will receive a reduced or failing grade for the assignment or other penalties may be imposed and the violation will be reported to the Honor Council.
Individual instructors may have additional requirements. Please consult the syllabus for your section for details.
Learning Outcomes
The primary learning outcome of this programming assignment is to review and reinforce content from CS149, such as writing code from a UML diagram including constructors, accessors, and mutators that make the use of basic programming constructs such as variables, declaration, assignment, conditionals, and loops as well as using the Java classes, Array and String. There are a few specific outcomes that may be new.
Resources
Download the file below, PlayScrabble.java, which implements a command line version of the game. You can use this
to see how the classes would work within the game. You should begin your development carefully, testing individual methods and classes as you write them.
New!
The following test classes are provided so that you can test using JUnit before you submit to Autolab.
New!
UML Diagram
The connectors in the UML diagram below represent *composition* and *aggregration* respectively. We'll be learning more about UML as the semester progresses. If you are interested in the details, you can check out this tutorial: UML Tutorial
Part 1 - Create Letter.java
Implement the class and methods according to the UML and specifications below.
Letter Constructor and Accessors
The constructor and accessors should be implemented to initialize letter and points
with the constructor parameters. The constructor should make sure that the letter is an upper case letter
of the English alphabet and that the point value is positive. If either of the arguments passed to the
constructor are not valid, the constructor should throw an IllegalArgumentException. See the section below on
Exceptions for more details on how to throw an exception when needed.
equals
The equals method should return true if the object passed is a Letter object and
both letter and points associated with this
Letter are equal to the corresponding letter and points of the obj Letter.
Otherwise false should be returned.
toString
The toString method should return a String describing the letter consisting of "Letter: " with one
space after the colon followed by the character, another space, then "Points: " followed by the points. For example the
String returned by a Letter with letter assigned 'T' and points assigned 3 will be:
"Letter: T Points: 3"
Part 2 - Create Hand.java
Implement the class and methods according to the UML and specifications below. When implementing these methods make sure to avoid code duplication by using other methods in the class or writing private helper methods as appropriate.
Hand()
The default constructor should create a hand of MAX_SIZE.
Hand(int size)
This constructor should create a hand of size. If size is less than zero, a hand of size zero should be created. If
size is greater than MAX_SIZE a hand of MAX_SIZE should be created.
insert
If index is within bounds and there is not another letter in the hand at index, the letter should be
inserted into the hand at index and return true. If those conditions do not hold, false
should be returned. If the index is out of bounds for this hand, an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException should be thrown.
remove
If index is within bounds, the letter at index should be removed from the hand (the location set to null)
and the letter that was at index returned. If there is no letter at index, return null. If the index is
out of bounds for this hand, an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException should be thrown.
indexOf
This method should search through the hand and return the index of the first occurrence of letter. If the letter is
not in the hand, return -1.
canForm
This method should determine if word can be formed from the letters in this hand. Return true if word can be formed
and false otherwise. If word is null a NullPointerException should be thrown.
toString
This method should return, for each index in the hand, the index followed by a colon, and then the Letter toString followed by a newline.
If there is no letter at index, i.e. the location is null, then insert a dash '-' where
the Letter toString would be printed. For example, the output from a hand of size 3, with a Letter B worth 1 point in index 0, no Letter in
index 1, and a Letter H worth 4 points in index 2 would be.
0: Letter: B Points: 1 1: - 2: Letter: H Points: 4
Part 3 - Create Board.java
Implement the class and methods according to the UML and specifications below.
Constructor
The constructor should create an "empty" board that is the same length of the multiplier parameter and use the
multiplier parameter to initialize the pointMult attribute. The pointMult attribute should be a copy of the multiplier array
(don't just copy the reference).
getLetter and getPointMult
These methods should get the value indicated by index. If index is out of bounds, an
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
should be thrown.
getBoardScore
This method should compute and return the score of the letters currently played on the board by multiplying the corresponding
indices of the point values of each letter in board and pointMult and adding them together.
play
This method should put letter into board at index and return true if
index is in bounds and there is no letter at index, false otherwise. If index is out of bounds, an
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
must be thrown.
fits
This method should return true if word will fit on the Board if it is placed starting at index and
false otherwise. A word does not fit on the board if it would extend past the last index or if it would
overlap with any letters that have already been placed. If index is out of bounds, an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
must be thrown.
getLetterScore
This method must return the point value of the letter at indexmultiplied by the multiplier at its Board location. If there
is no letter at indexit must return zero. If index is out of bounds, an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException must
be thrown.
toString
This method should return a String representing the board. Each index in the board should be represented by two lines. One with the
index of the board location and the Letter, and the second representing the multiplier. The line representing the letter should be
the index, followed by a colon, followed by a space, followed by the toString for the letter or a dash if there is no letter.
The second line should be the word
"Multiplier" followed by a colon and the pointMult at that index. For example a board of length 4 with a letter
at index 1 with a character value of 'A' and a point value of 10 and a pointValue array with values {1,2,3,4).
0: - Multiplier: 1 1: Letter: A Points: 10 Multiplier: 2 2: - Multiplier: 3 3: - Multiplier: 4
Part 4 - Submitting Through Autolab
- Make sure and use the provided test classes to test your code locally before submitting to Autolab. Your Autolab submissions will be limited.
- Navigate to http://Autolab.cs.jmu.edu and log-in.
- Zip the files
Letter.java,Hand.java, andBoard.javaand upload the file to Autolab. Remember to zip the individual files and NOT the folder the files are in. - If your code fails any of the submission tests, make any necessary modifications and resubmit until there are no failures.
Hints
Below are hints to help you write your code.
Exceptions
According to the Java Tutorials, "An exception is an event, which occurs during the execution of a program, that disrupts the normal flow of the program's instructions.
There are times when we do not want to indicate a problem in a method by a different return value, either because there may not be
an appropriate error value to return or because the method itself does not know how to fix the problem. In these cases a method can "throw"
an object called an exception to let the calling program know of the error condition. The calling program can either handle that exception
or end the program. This assignment asks you to "throw" an IllegalArgumentException. It also specifies that some methods will
"throw" either an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException or NullPointerException. Note that you do not need to write code for the latter two exceptions, they
are "thrown" by the runtime system. Later in the course we will learn how to handle
exceptions, but in this case the program will just end with the error.
To throw an exception, use the keyword throw followed by creating an exception.
For example:
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
For more details see The Java Tutorial Page on throwing exceptions.
Note that you will not need to throw every exception as specified on this assignment. Some exceptions are thrown automatically. Think carefully about when you will need to check for specific errors and when you won't.
StringBuilder
Note that StringBuilder might be useful for implementing the toString methods. See this explanation
in ThinkJava for why
you might want to use StringBuilder instead of String.