Impact of Load Factor on Cost
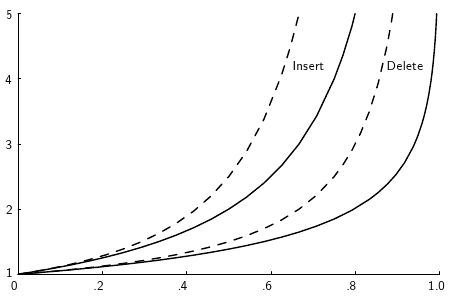
Dashed lines are linear probing, solid lines are “random” probing.
Load factor is on the x-axis, expected number of buckets accessed on the y-axis.
(From OpenDSA book)
When a class overrides equals it should also override hashCode. Consider the following hashCode implementation:
Assuming the HashTable implementation from last week’s lab, how will this hashCode function perform in practice?

Dashed lines are linear probing, solid lines are “random” probing.
Load factor is on the x-axis, expected number of buckets accessed on the y-axis.
(From OpenDSA book)
Which of the following best describes the corresponding figure when chaining is used for collision resolution? (load factor on the x-axis, expected number of key comparisons on the y-axis).
perturb is initialized to the original hash, then bit-shifted after every collision.Implementation in: Python-2.7.2/Objects/dictobject.c. Source can be downloaded from www.python.org.
Update in Python 3:
the dictionary:
d = {'timmy': 'red', 'barry': 'green', 'guido': 'blue'}
is currently stored as:
entries = [['--', '--', '--'],
[-8522787127447073495, 'barry', 'green'],
['--', '--', '--'],
['--', '--', '--'],
['--', '--', '--'],
[-9092791511155847987, 'timmy', 'red'],
['--', '--', '--'],
[-6480567542315338377, 'guido', 'blue']]
Instead, the data should be organized as follows:
indices = [None, 1, None, None, None, 0, None, 2]
entries = [[-9092791511155847987, 'timmy', 'red'],
[-8522787127447073495, 'barry', 'green'],
[-6480567542315338377, 'guido', 'blue']]
Only the data layout needs to change. The hash table
algorithms would stay the same.descripion: https://mail.python.org/pipermail/python-dev/2012-December/123028.html
source: https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/main/Objects/dictobject.c
Original source: https://github.com/ruby/ruby/blob/ruby_2_3/st.c Current source: https://github.com/ruby/ruby/blob/ruby_3_0/st.c
static int hash(int h) {
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}Java 16 Source: https://github.com/openjdk/jdk/blob/jdk-16+36/src/java.base/share/classes/java/util/HashMap.java