Programming Assignment #1: JMUahoogling
(The World's Greatest Search Engine)
Introduction
Your objective for this assignment is to build a simple text-based search engine in Python.
A search engine has three main components:
- The Index stores a mapping from possible search terms to web-pages that contain those terms. Commercial search engines like Google or Yahoo use highly optimized, highly parallel, special-purpose databases containing many terabytes of data. We'll use a Python dictionary to store the index.
- The Crawler systematically downloads HTML documents in order to gather data for the index. A web crawler finds documents by following links, in much the same way you do when you surf the web.
- The Ranking Function provides a mechanism for ordering results in cases where more than one match is found. Google became a multi-zillion dollar company by introducing a better ranking function (PageRank) than other companies were using at the time.
Utility Code
As a starting point, we have provided a utility module
named crawler_util.py that contains
the HTMLGrabber class. This class will handle some of the
messy details of networking in Python and parsing HTML. Here is an
abbreviated version of the documentation of for that class:
class HTMLGrabber(HTMLParser.HTMLParser)
| This class handles downloading and processing an HTML document.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __init__(self, url, verbose=False)
| Construct an HTMLGrabber object.
|
| This constructor downloads the HTML file at the indicated
| address and parses it in order to extract the page title, the
| page text and all outgoing links.
|
| Notes:
| - robots.txt is respected. If the server doesn't want the
| file crawled, this function won't crawl it.
| - If any sort of exception occurs during processing, this
| function will quietly give up and subsequent calls to
| get_text etc. will return empty defaults.
|
| Parameters:
| url - A string containing a valid absolute url. Eg:
| "http://www.jmu.edu" or
| "file:///home/spragunr/somefile.html"
| verbose - If True, an error message will be printed if an
| exception is encountered. If False, exceptions
| are quietly ignored. Defaults to False.
|
| get_links(self)
| Return all outgoing links from the HTML document.
|
| Notes:
| - Only one copy of each link will be returned.
| - All links are returned. Returned links may or may not refer
| to HTML documents.
|
| Returns:
| An unordered list of strings, where each string is a URL.
|
| get_text(self)
| Return all of the document text as a single lower-case string.
| All Punctuation will be removed. This may return an empty
| string if there were errors during parsing.
|
| get_title(self)
| Return the HTML page title. This may return an empty string
| if there were errors during parsing, or if the page has no
| title.
|
| get_url(self)
| Returns a string containing the URL of this page.
Here is an example of using this class from within the Python interpreter:
Python 3.4.1 (v3.4.1:c0e311e010fc, May 18 2014, 00:54:21)
[GCC 4.2.1 (Apple Inc. build 5666) (dot 3)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import crawler_util
>>> grabber = crawler_util.HTMLGrabber("http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/")
>>> print(grabber.get_title())
Data Structures And Algorithms
>>> print(grabber.get_url())
http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/
>>> print(grabber.get_text())
cs 240 data structures and algorithms james madison university fall 2014
instructor nathan sprague meeting times section 1 meets mwf 9 05 9 55 isat
cs 243 section 2 meets mwf 10 10 11 00 isat cs243 syllabus detailed schedule
canvas supplemental material obligatory xkcd comic
>>> print(grabber.get_links())
['http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/syllabus.shtml', 'http://www.jmu.edu/',
'https://canvas.jmu.edu/', 'http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/',
'http://xkcd.com/353/', 'http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/schedule.shtml',
'http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/supplement.shtml',
'http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/']
I recommend that you get started on this project by playing around with the
HTMLGrabber class in the terminal until you have a good
understanding of how it works. If you completed the dictionaries lab, you will already have some
experience working with this class. If you have not already done so, I highly
recommend finishing it.
The SearchEngine Class
Your main task for this project is to complete a simple web crawler and
search engine. The project skeleton has been provided in the file engine.py. Download that file, read it
carefully, and use it as the basis for your submission.
As your primary assignment, you will provide the implementation for the
SearchEngine class. You are free to add as many instance variables
and methods to this class as you like. However, you may not change the method
signatures of the three existing methods that you will need to complete
according to the specifications provided in the docstrings:
def __init__(self): """ Construct a SearchEngine. At the time of construction the index is empty. """ # YOUR CODE HERE You will (at least) need someplace to store # the search index (I suggest a dictionary) and some way of # keeping track of which URLs have already been crawled (I # suggest a set). pass # pass is a do-nothing instruction. It's just here because # it is a syntax error in Python to have an empty code block. # Replace it with good code. def crawl(self, url, max_depth): """ Update the index by crawling a collection of HTML documents. The crawl begins at url and will visit all pages within max_depth links. For example, if max_depth = 0, only the document located at the indicated url is indexed. If max_depth = 2, the original document is indexed, along with all documents that it links to and all of the documents that THOSE documents link to. This method tracks which URLs have already been visited so that no URL will be processed more than once. Arguments: url - A string containing a valid URL. For example: "http://www.jmu.edu" or "file:///home/spragunr/somefile.html" max_depth - The maximum crawl depth. See explanation above. No return value. """ # YOUR CODE HERE pass def search(self, word): """ Return a list of SearchResult objects that match the given word. This function returns a (possibly empty) list of SearchResult objects. Each object refers to a document that contains the indicated word. The search is NOT case sensitive. This method will accept any string, but assumes that the string represents a single word. Since the index only stores individual words, any strings with spaces or punctuation will necessarily have 0 hits. Arguments: word - A string to search for in the search engine index. Return: A list of SearchResult objects. The order of the objects in the list is not specified. """ #YOUR CODE HERE. pass
Of the three methods, crawl() will be the most challenging to
complete. The __init__() and search() methods should
only be a few lines of code each. The easiest way to implement
crawl() is to use recursion. Crawling
is inherently recursive: you crawl a web page by visiting the page, then
crawling all of the linked pages. The following pseudocode captures the basic
idea:
Crawling the web starting at URL:
Record the fact that this URL has been crawled.
Download all of the text from the URL and update the index.
Download all of the links from the URL.
For each downloaded link that hasn't been crawled yet:
Recursively crawl starting at that link.
There is one problem with this algorithm: it won't terminate until all pages reachable from the starting URL have been indexed. In most cases, this will represent a large percentage of the World Wide Web. As you probably know, the web is big. Your program would run out of memory long before it finished crawling.
The SearchEngine class addresses this issue by allowing us to put a limit on the maximum number of links that are followed from the starting URL to any other URL. Implementing this limit requires only a slight modification (marked with "***") to the above algorithm:
Crawling the web starting at URL:
Record the fact that this URL has been crawled.
Download all of the text from the URL and update the index.
Download all of the links from the URL.
If continuing to crawl won't exceed the depth limit: (***)
For each downloaded link that hasn't been crawled yet:
Recursively crawl starting at that link.
User Interface
The class described above provides the back-end functionality for a search engine, but it doesn't provide a friendly user interface. Ideally, we would set up a web-based interface and get rich from advertising revenue. In the interest of time, we'll just create a text-based interface as a proof of concept. You interface should:- Prompt the user for a URL to start crawling.
- Prompt the user for a maximum crawl depth.
- Respond to user queries with lists of matching URLs from the crawled pages.
- Exit whenever the user enters an empty query.
An interaction with your crawler should look like the following. The text formatting and prompts should be exactly the same as the example below. The ordering of the results need not be the same.
$ python3 engine.py
Enter URL to crawl: http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/
Depth: 1
Enter search term: stacks
Results:
Data Structures And Algorithms: Syllabus
http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/syllabus.shtml
CS240 Schedule
http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/schedule.shtml
Enter search term: Python
Results:
xkcd: Python
http://xkcd.com/353/
Data Structures And Algorithms: Syllabus
http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/syllabus.shtml
Data Structures And Algorithms: Supplemental Material
http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/supplement.shtml
CS240 Schedule
http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/schedule.shtml
Enter search term: [USER PRESSES ENTER]
Thank you for using JMUahoogling!
Your user interface code should be in a function called main,
and you should include the standard Python idiom for calling the
main function:
if "__name__" == "__main__":
main()
Remember that the above snippet should be located at the end of the file and should not be indented.
Testing
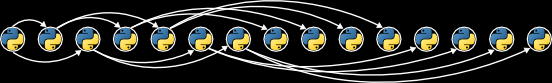
In order to facilitate testing, I am providing a small collection of web pages that contains no links to outside pages. The following diagram illustrates the file names of the pages, the contents of the pages, and the link structure:
For example, trees.html is a page with only two words:
"Ash" and "Maple". It contains only a single outgoing link to
streets.html. You can browse these pages
here: http://w3.cs.jmu.edu/spragunr/CS240/activities/crawler/simple/trees.html.
You are welcome to use that URL in your testing, but it may be more
convenient to download a local copy of those pages, and test on your
own computer. First download and unzip the
file simple.zip. You can then create a URL
that specifies a location on the local machine using
the file scheme. For example, on my own computer, I
might use:
"file:///home/spragunr/simple/trees.html"
On your computer you will need to replace "/home/spragunr/" with the absolute path to the directory where you saved the web pages.
I recommend that you get your code working on these pages before you
turn it loose on the web at large. When you do test your code on the
web, you'll probably need to restrict your crawling depth to 2 or 3 at
the most. If we assume that most web pages have around 10 outgoing
links (a conservative estimate), then a crawl of depth three will
traverse:
1 (the initial page) +
10 (all linked pages) +
100
(all pages linked from those pages.) +
1000 (etc.) = 1111
total pages.
Handing In
You should submit the fileengine.py by the deadline. You
should not submit crawler_util.py. Your code
should conform to the CS240 Python
Coding Conventions.