|
Visual Content
An Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
|
Visual Content
An Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein |
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |
An EM Wave
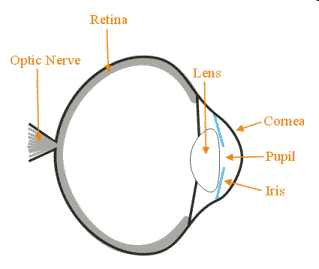
The Eye
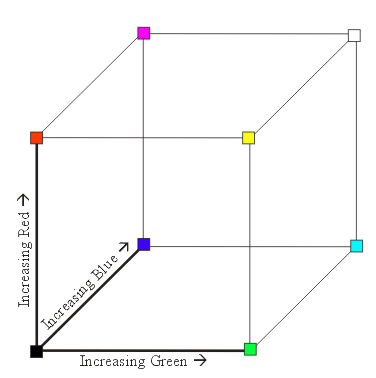
The (Linear) Color Cube
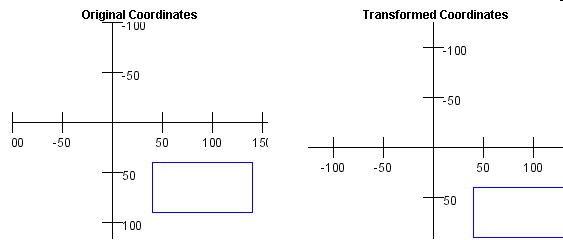
A Translation of (25,25)
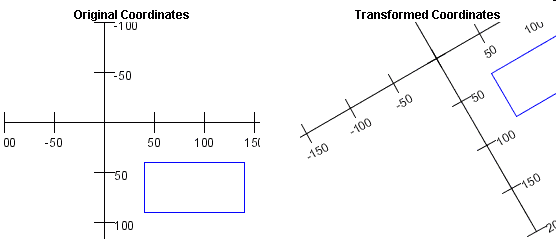
A Rotation of \(- \pi / 6\) Radians
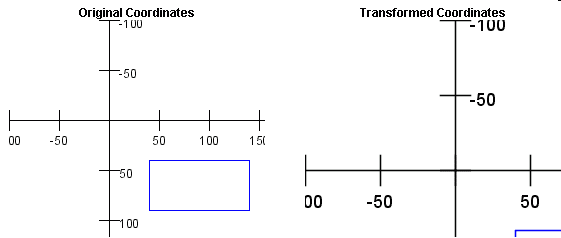
A Scaling of (1.5, 1.5)
A Reflection About the Horizontal Axis
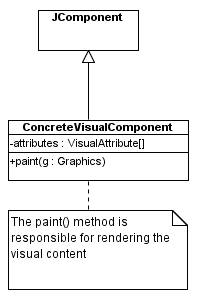
JComponent Class:
paint(java.awt.Graphics)
method is called and is passed a rendering engine
JComponent
paint() methodAn Example
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A concrete extension of a JComponent that illustrates
* the process of obtaining and using a rendering engine
*
* @version 1.0
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
*/
public class BoringComponent extends JComponent
{
/**
* Render this BoringComponent
*
* @param g The rendering engine to use
*/
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2;
// Cast the rendering engine appropriately
g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
// Put the rendering code here
}
}
JComponent can be added
to the content pane of a MultimediaApplication
or MultimediaApplet
A Common Design
A Design with a Problem
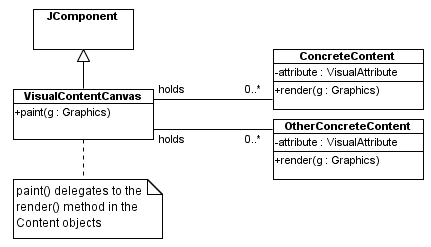
A Better Design
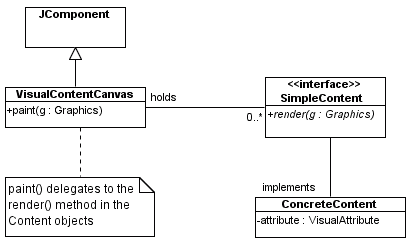
A Design that Satisfies Almost All of the Requirements
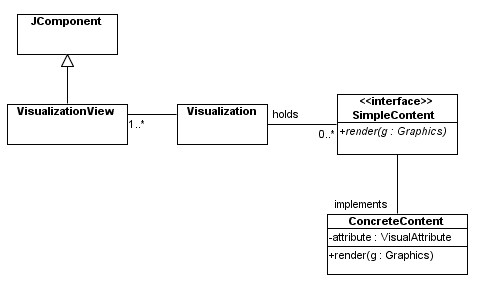
"Enhancing" the View with Specialization
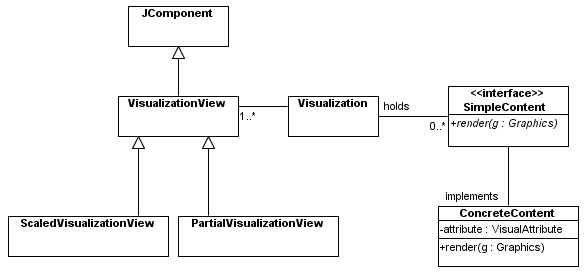
A Good Design
SimpleContent Interfacepackage visual.statik;
import java.awt.*;
/**
* The requirements of simple static visual content
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface SimpleContent
{
/**
* Render this static visual content
*
* @param g2 The rendering engine to use
*/
public abstract void render(Graphics g);
}
Visualization ClassSkeleton:
package visual;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
import visual.statik.SimpleContent;
/**
* A collection of Content objects to be rendered
* (and a collection of GUI components that will
* render them)
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Visualization
{
private CopyOnWriteArrayList<SimpleContent> content;
private LinkedList<VisualizationView> views;
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public Visualization()
{
content = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<SimpleContent>();
views = new LinkedList<VisualizationView>();
views.addFirst(createDefaultView());
}
}
Content Management:
/**
* Add a SimpleContent to the "front" of this Visualization
*
* Note: This method only adds the SimpleContent if it is not
* already in the Visualization. However, the "underlying"
* content (e.g., BufferedImage, Shape) in two different
* SimpleContent objects can be the same.
*
* To change the order of a SimpleContent that is already on the canvas
* use toBack() or toFront().
*
* @param r The SimpleContent to add
*/
public void add(SimpleContent r)
{
if (!content.contains(r))
{
content.add(r);
repaint();
}
}
/**
* Clear this Visualization of all SimpleContent objects
*/
public void clear()
{
content.clear();
}
/**
* Get an Iterator that contains all of the SimpleContent
* objects
*
* @return The SimpleContent objects
*/
public Iterator<SimpleContent> iterator()
{
return content.iterator();
}
/**
* Remove the given SimpleContent from this Canvas
*
* @param r The SimpleContent to remove
*/
public void remove(SimpleContent r)
{
if (content.remove(r)) repaint();
}
/**
* Move the given SimpleContent to the "back"
*
* Note: The SimpleContent must have already been added for this
* method to have an effect.
*
* @param r The SimpleContent to move to the back
*/
public void toBack(SimpleContent r)
{
boolean removed;
removed = content.remove(r);
if (removed)
{
content.add(r);
}
}
/**
* Move the given SimpleContent to the "front".
*
* Note: The SimpleContent must have already been added for this
* method to have an effect.
*
* @param r The SimpleContent to move to the front
*/
public void toFront(SimpleContent r)
{
boolean removed;
removed = content.remove(r);
if (removed)
{
content.add(0, r);
}
}
View Management:
/**
* Add a view to this Visualization
*
* @param view The view to add
*/
public void addView(VisualizationView view)
{
views.addLast(view);
}
/**
* Get the "main" view (i.e., the "main" VisualizationView
* that is used to present the SimpleContent objects) associated
* with this Visualization.
*
* Note: A visualization can actually have multiple
* views associated with it. This is a convenience
* method that can be used when there is only one such
* view.
*
* @return The view
*/
public VisualizationView getView()
{
return views.getFirst();
}
/**
* Get all of the views associated with this Visualization
*
* @return The views
*/
public Iterator<VisualizationView> getViews()
{
return views.iterator();
}
/**
* Remove a view from this Visualization
*
* @param view The view to remove
*/
public void removeView(VisualizationView view)
{
views.remove(view);
}
/**
* Change the "main" view associated with this Visualization
*
* Note: A visualization can actually have multiple
* views associated with it. This is a convenience
* method that can be used when there is only one such
* view.
*
* @param view The new view to use as the "main" view
*/
public void setView(VisualizationView view)
{
views.removeFirst();
views.addFirst(view);
}
Forcing Rendering:
/**
* Repaint the view(s) assocaited with this Visualization
*/
protected void repaint()
{
Iterator<VisualizationView> i;
VisualizationView view;
i = views.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
view = i.next();
view.repaint();
}
}
VisualizationView ClassSkeleton:
package visual;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import visual.statik.*;
/**
* A GUI component that presents a collection of SimpleContent
* objects
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class VisualizationView
extends JComponent
implements MouseListener
{
protected Visualization model;
protected VisualizationRenderer renderer;
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param model The Visualization to use
* @param renderer The VisualizationRenderer to use
*/
public VisualizationView(Visualization model,
VisualizationRenderer renderer)
{
super();
this.model = model;
this.renderer = renderer;
}
/**
* Handle updates
*
* This is overriden so that the background is not
* erased before painting (which is the default)
*/
public void update(Graphics g)
{
paint(g);
}
}
Rendering:
/**
* Set the VisualizationRenderer that this component
* should use when rendering
*
* @param renderer The VisualizationRenderer
*/
public void setRenderer(VisualizationRenderer renderer)
{
this.renderer = renderer;
}
/**
* Operations to perform after rendering.
* This method is called by paint().
*
* @param g The rendering engine
*/
protected void postRendering(Graphics g)
{
renderer.postRendering(g, model, this);
}
/**
* Operations to perform before rendering.
* This method is called by paint().
*
* @param g The rendering engine
*/
protected void preRendering(Graphics g)
{
renderer.preRendering(g, model, this);
}
/**
* Render the content contained in the model.
* This method is called by paint().
*
* @param g The rendering engine
*/
protected void render(Graphics g)
{
renderer.render(g, model, this);
}
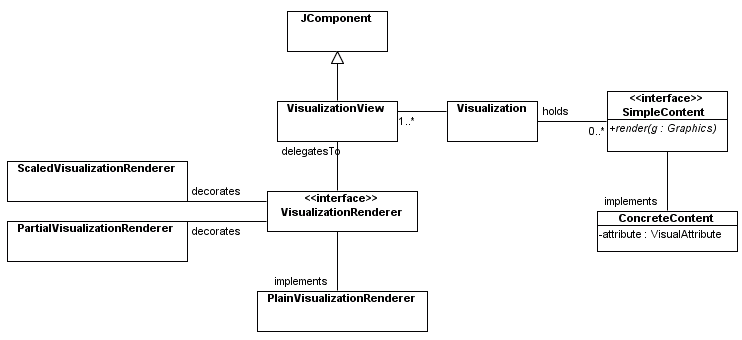
PlainVisualizationRenderer Class
/**
* Render the content contained in the model.
* This method is called by paint().
*
* @param g The rendering engine
*/
public void render(Graphics g,
Visualization model,
VisualizationView view)
{
Iterator<SimpleContent> iter;
SimpleContent c;
iter = model.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext())
{
c = iter.next();
if (c != null) c.render(g);
}
}
ScaledVisualizationRenderer ClassSkeleton:
package visual;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* A decorator of a VisualizationRenderer that adds
* scaling capabilities. That is, a ScaledVisualizationRenderer
* will scale all of the content to fit its component.
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class ScaledVisualizationRenderer
implements VisualizationRenderer
{
private double height, scaleX, scaleY, width;
private VisualizationRenderer decorated;
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param decorated The VisualizatioRenderer to decorate
* @param width The full-size width of the content
* @param height The full-size height of the content
*/
public ScaledVisualizationRenderer(VisualizationRenderer decorated,
double width, double height)
{
this.decorated = decorated;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
/**
* Render the content contained in the model.
*
* @param g The rendering engine
* @param model The Visualization containing the content
* @param view The component presenting the content
*/
public void render(Graphics g,
Visualization model,
VisualizationView view)
{
decorated.render(g, model, view);
}
}
Before Rendering:
/**
* Operations to perform before rendering.
*
* @param g The rendering engine
* @param model The Visualization containing the content
* @param view The component presenting the content
*/
public void preRendering(Graphics g,
Visualization model,
VisualizationView view)
{
Dimension size;
Graphics2D g2;
g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
size = view.getSize();
scaleX = size.getWidth() / width;
scaleY = size.getHeight() / height;
g2.scale(scaleX, scaleY);
decorated.preRendering(g, model, view);
}
After Rendering:
/**
* Operations to perform after rendering.
*
* @param g The rendering engine
* @param model The Visualization containing the content
* @param view The component presenting the content
*/
public void postRendering(Graphics g,
Visualization model,
VisualizationView view)
{
Graphics2D g2;
g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
g2.scale(1.0/scaleX, 1.0/scaleY);
decorated.postRendering(g, model, view);
}
PartialVisualizationRenderer ClassSkeleton:
package visual;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* A decorator of a VisualizationRenderer that
* only shows part of the content.
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public class PartialVisualizationRenderer
implements VisualizationRenderer
{
private double x, y;
private VisualizationRenderer decorated;
/**
* Explicit Value Constructor
*
* @param decorated The VisualizatioRenderer to decorate
* @param x The left-most point to render
* @param y The upper-most point to render
*/
public PartialVisualizationRenderer(VisualizationRenderer decorated,
double x, double y)
{
this.decorated = decorated;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
/**
* Render the content contained in the model.
*
* @param g The rendering engine
* @param model The Visualization containing the content
* @param view The component presenting the content
*/
public void render(Graphics g,
Visualization model,
VisualizationView view)
{
decorated.render(g, model, view);
}
}
Before Rendering:
/**
* Operations to perform before rendering.
*
* @param g The rendering engine
* @param model The Visualization containing the content
* @param view The component presenting the content
*/
public void preRendering(Graphics g,
Visualization model,
VisualizationView view)
{
Graphics2D g2;
g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
g2.translate(-x, -y);
decorated.preRendering(g, model, view);
}
After Rendering:
/**
* Operations to perform after rendering.
*
* @param g The rendering engine
* @param model The Visualization containing the content
* @param view The component presenting the content
*/
public void postRendering(Graphics g,
Visualization model,
VisualizationView view)
{
Graphics2D g2;
g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
g2.translate(x, y);
decorated.postRendering(g, model, view);
}
Transformation class that contains
the necessary attributes and behaviorsSimpleContent
Adding Transformations using a Helper
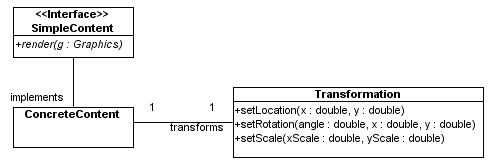
Adding Transformations using Stand-Alone Interfaces
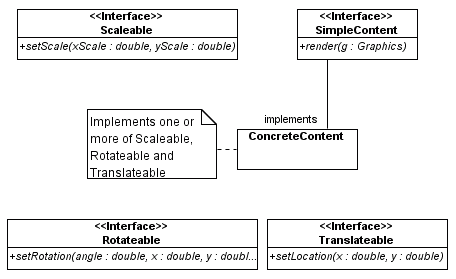
Adding Transformations using Individual Interfaces
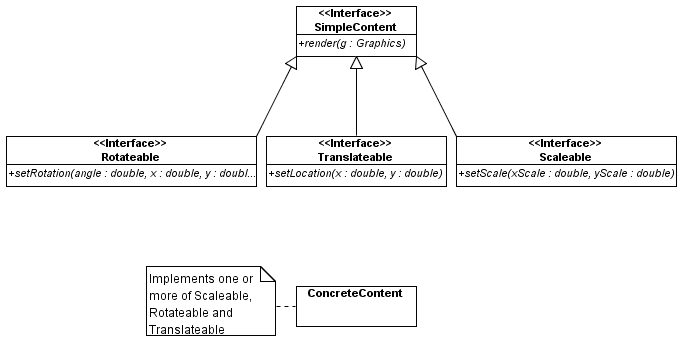
The Best Way to Add Transformations
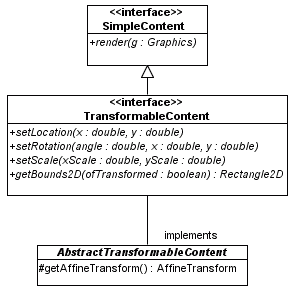
AbstractTransformableContent Classpackage visual.statik;
import java.awt.geom.*;
/**
* A partial implementation of the TransformableContent
* interface that keeps track of transformation information
*
* @author Prof. David Bernstein, James Madison University
* @version 1.0
*/
public abstract class AbstractTransformableContent
implements TransformableContent
{
protected boolean relocated, rerotated, rescaled;
protected double angle;
protected double xScale, yScale;
protected double x, y;
protected double xRotation, yRotation;
/**
* Default Constructor
*/
public AbstractTransformableContent()
{
setTransformationRequired(false);
angle = 0.0;
xScale = 1.0;
yScale = 1.0;
x = 0.0;
y = 0.0;
xRotation = 0.0;
yRotation = 0.0;
}
/**
* Get the (concatenated) AffineTransform
*
* @return The rotation, scaling and translation concatenated
*/
protected AffineTransform getAffineTransform()
{
// We could use an object pool rather than local
// variables. Rough tests estimate that this method
// would require 1/3 as much time with an object pool.
AffineTransform at, rotation, scaling, translation;
Rectangle2D bounds;
// Start with the identity transform
at = AffineTransform.getTranslateInstance(0.0, 0.0);
if (rerotated)
{
bounds = getBounds2D(false);
rotation = AffineTransform.getRotateInstance(angle,
xRotation,
yRotation);
at.preConcatenate(rotation);
}
if (rescaled)
{
scaling = AffineTransform.getScaleInstance(xScale,
yScale);
at.preConcatenate(scaling);
}
if (relocated)
{
translation = AffineTransform.getTranslateInstance(x,
y);
at.preConcatenate(translation);
}
return at;
}
/**
* Returns a high precision bounding box of the appropriately
* transformed content (required by TransformedContent)
*
* @return The bounding box
*/
public Rectangle2D getBounds2D()
{
return getBounds2D(true);
}
/**
* Returns a high precision bounding box of the Content
* either before or after it is transformed
*
* @param transformed true to get the BB of the transformed content
* @return The bounding box
*/
public abstract Rectangle2D getBounds2D(boolean transformed);
/**
* Set the translation
* (required by TransformedContent)
*
* @param x The x posiiton
* @param y The y position
*/
public void setLocation(double x, double y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
relocated = true;
}
/**
* Set the angle of rotation around the midpoint
* (required by TransformedContent)
*
* @param angle The rotation angle
* @param x The x-coordinate of the point to rotate around
* @param y The y-coordinate of the point to rotate around
*/
public void setRotation(double angle, double x, double y)
{
this.angle = angle;
xRotation = x;
yRotation = y;
rerotated = true;
}
/**
* Set the scaling
* (required by TransformedContent)
*
* @param xScale The scaling in the horizontal dimension
* @param yScale The scaling in the vertical dimension
*/
public void setScale(double xScale, double yScale)
{
this.xScale = xScale;
this.yScale = yScale;
rescaled = true;
}
/**
* Set the scaling
*
* @param scale The scaling (in both dimensions)
*/
public void setScale(double scale)
{
setScale(scale, scale);
}
/**
* Set whether this AbstractTransformableContent object
* needs to be transformed before being used
*
* @param required true to indicate that a transformation is requried
*/
protected void setTransformationRequired(boolean required)
{
relocated = required;
rerotated = required;
rescaled = required;
}
/**
* Does this AbstractTransformableContent object need
* to be transformed before being used?
*
* @return true to indicate a transformation is required
*/
protected boolean isTransformationRequired()
{
return (relocated || rerotated || rescaled);
}
}