Vector Graphics
A Simplified Approach with Examples in Java
|
|
Prof. David Bernstein
James Madison University
|
|
|
Computer Science Department
|
|
bernstdh@jmu.edu
|

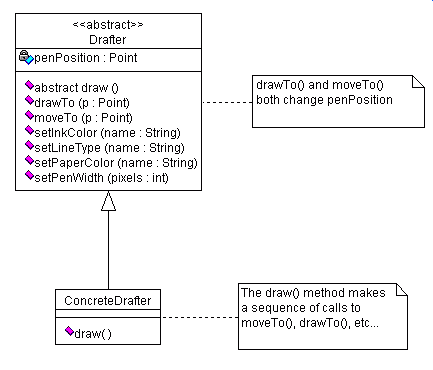
A ConcreteDrafter



A Floor Plan
javaexamples/navigation/FloorPlanExample.java
Drawing Features



LineSegment
javaexamples/navigation/FeatureDrafter1.java
(Fragment: 1)
Drawing Features (cont.)



PiecewiseLinearCurve
javaexamples/navigation/FeatureDrafter1.java
(Fragment: 2)
Drawing Features (cont.)



Polygon
javaexamples/navigation/FeatureDrafter1.java
(Fragment: 3)
Drawing Features (cont.)



All Classes that Implement Feature
javaexamples/navigation/FeatureDrafter2.java
(Fragment: 1)
The Rectangular Hull (cont.)



One Possible Implementation
javaexamples/navigation/RectangularHull.java
Drawing Re-sized Features



javaexamples/navigation/FeatureDrafter3.java
(Fragment: 1)
There's Always More to Learn