

|
Images/Rasters
An Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |



|
Images/Rasters
An Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |

















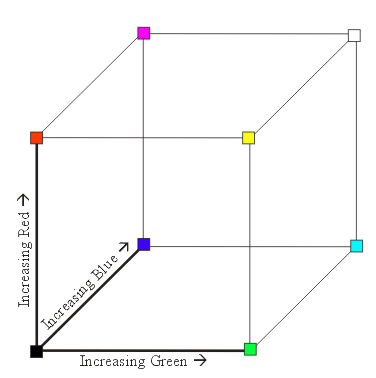
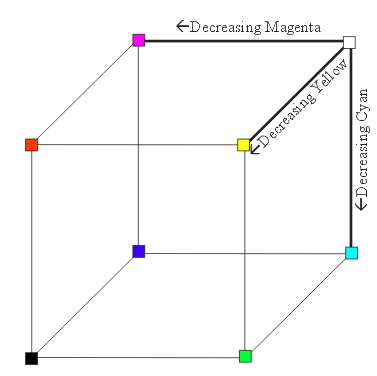


\( \left[ \begin{array}{c c} Y \\ I \\ Q \end{array} \right] = \left[ \begin{array}{r r r} 0.299 & 0.587 & 0.114 \\ 0.596 & -0.275 & -0.321 \\ 0.212 & -0.523 & 0.311 \\ \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{c c} R \\ G \\ B \end{array} \right] \)
\( \left[ \begin{array}{c c} R \\ G \\ B \end{array} \right] = \left[ \begin{array}{r r r} 1.000 & 0.956 & 0.621 \\ 1.000 & -0.272 & -0.647 \\ 1.000 & -1.105 & 1.702 \\ \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{c c} Y \\ I \\ Q \end{array} \right] \)



