|
Pointers and References in C/C++
An Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |



|
Pointers and References in C/C++
An Introduction |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |





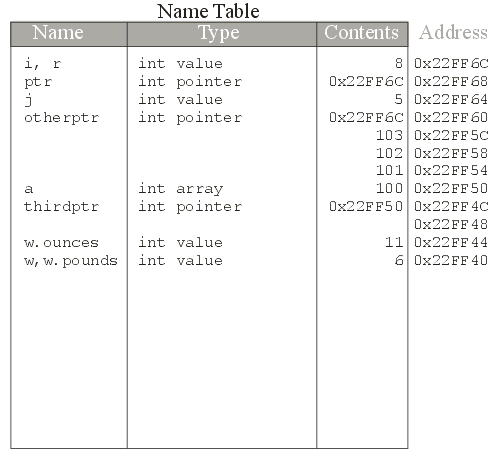
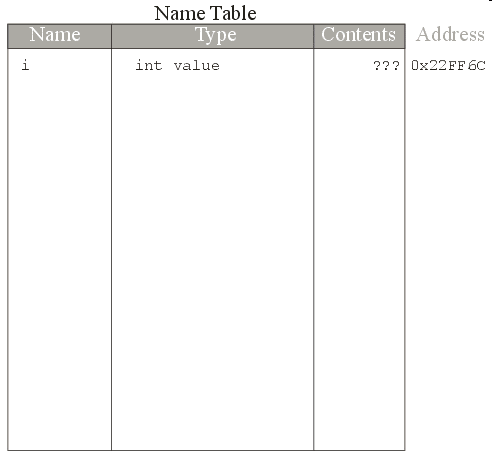
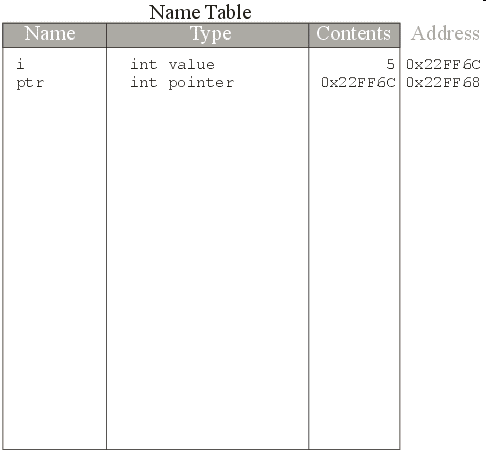
int i;
i is added to the name tablei is designated a value typeint
&i


i = 5;
i is assigned the value 5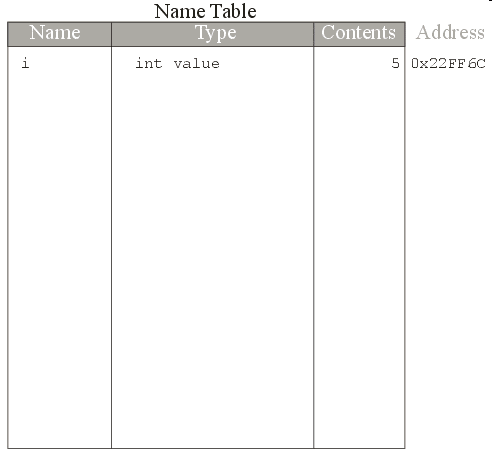


*
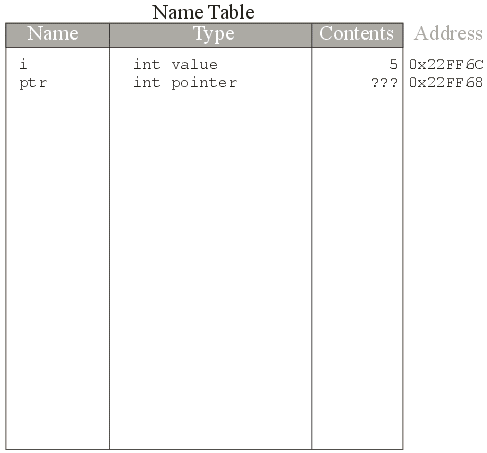
int *ptr;
&ptr


ptr = &i;


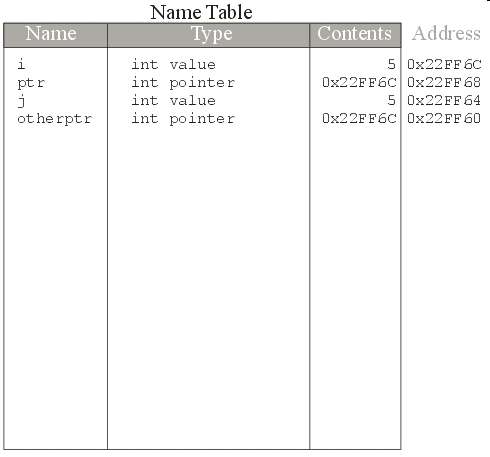
* operator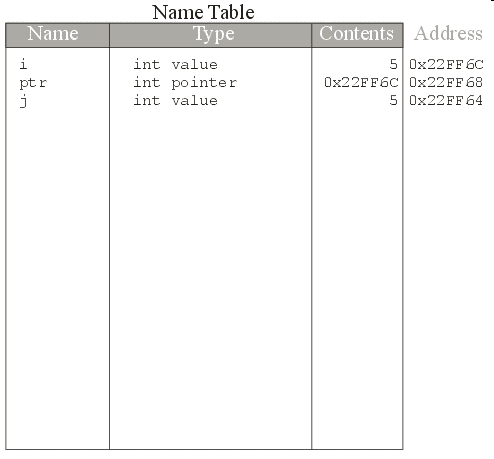




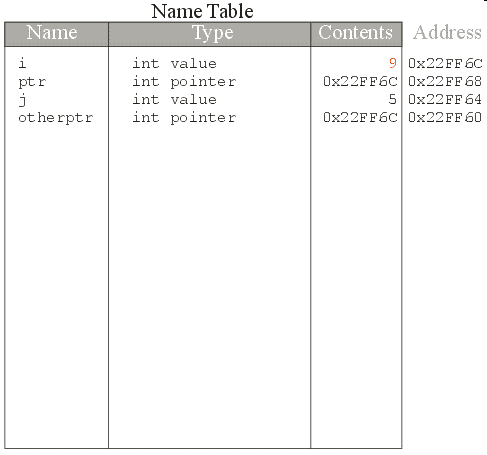
(*otherptr) = 9;


int a[4];
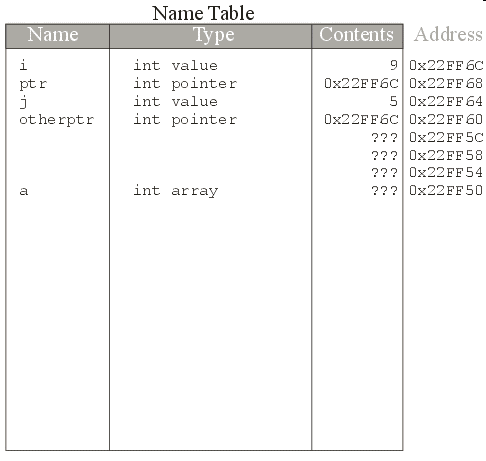


a,
&a and &a[0]
all evaluate to the same thingsizeof and
&)[] is evaluated before
&


int array is an int
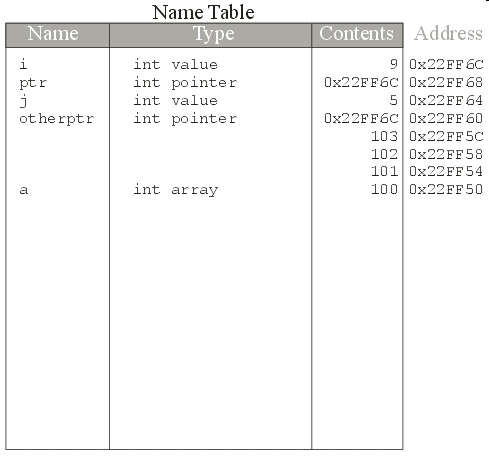


int
array is a pointer to an int




int
does not change its contents by 1, it changes
its contents by the size of the data type
it is pointing to
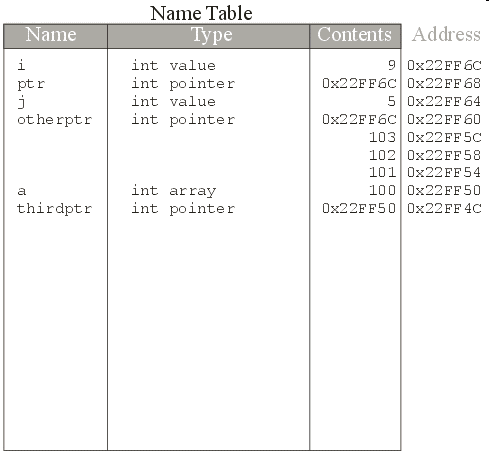
thirdptr+1 is 0x22FF54
*(thirdptr) is the same as a[0]
*(thirdptr+1) is the same as a[1]
*(thirdptr+2) is the same as a[2]
*(thirdptr+3) is the same as a[3]


&


r now refers to i so
it has the same address and the same contents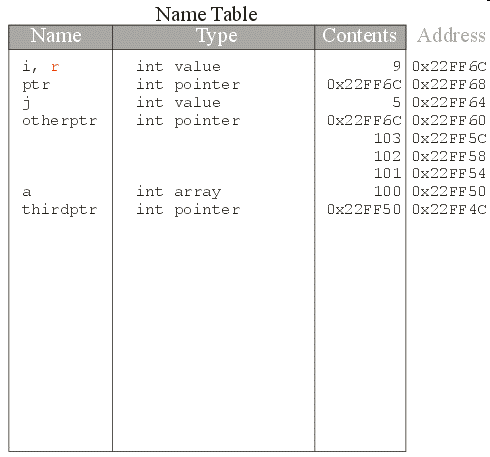




Weight object, its
constructor is called, and the two member attributes
are initialized