

|
Type-Safe/Parameterized Collections
in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |



|
Type-Safe/Parameterized Collections
in Java |
|
Prof. David Bernstein
|
| Computer Science Department |
| bernstdh@jmu.edu |







java.util.List Interface

void add(int index, E element)
E get(int index)
E set(int index, E element)
int size()
java.util.Map Interface

Object as
an index/key
V get(K key)
V put(K key, V value)
int size()
java.util.Map Interface (cont.)

Object
(since it can be used as the key in a Map)
Object has a
hashCode() method
that can be used for this purpose (which can be based on
the object's address, but needn't be)




Object objects in a
collection
Object to the
appropriate type when you retrieve it



The parameters for the class are listed (in order) in the dotted rectangle and are used as types elsewhere.
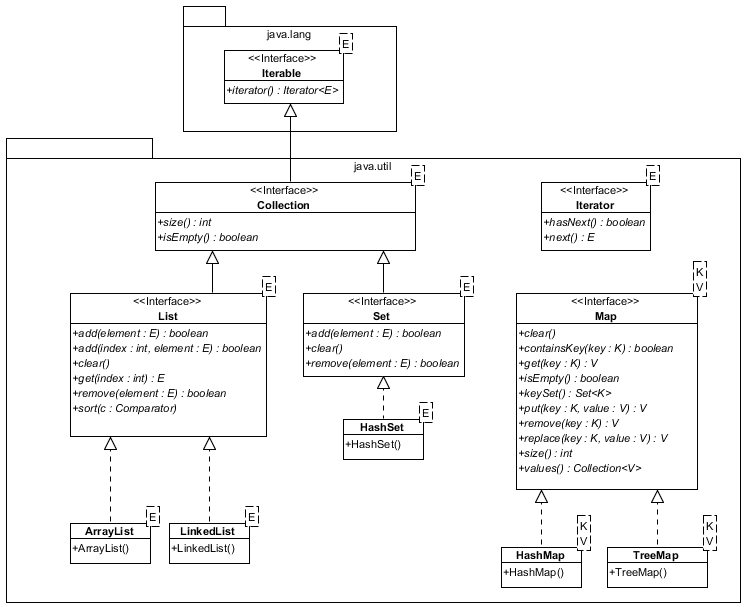
Note that parameters are not explicitly included in constructors.
Note also that bound parameters are included in arguments or return types
(e.g., the keySet() method returns a Set of
K so it is written as Set<K>). Note
finally that Map is not "officially"
a Collection (for reasons we will discuss later).


add() (in List)
and put() (in Map):
Object
List and a Map can only
contain class typesint, double,
etc...

Integer:
Integer(int value)
Integer.valueOf(int value)
int intValue()
Double:
Double(double value)
Double.valueOf(double value)
double doubleValue()




OptionalInt and OptionalDouble:
boolean isPresent()
int orElse(int default) and double orElse(double default) return the value if present and the default otherwise





SecurityQuotation
class and two subclasses, StockQuotation
and FutureQuotation
ArrayList) that contains children
of both types?



StockQuotation object to
a variable that is declared to be a
SecurityQuotation (because
a StockQuotation "is a"
SecurityQuotation)
ArrayList<StockQuotation>
to a variable of type
ArrayList<SecurityQuotation>?



? is called the wildcard character



