
| (1) | _____ |
A 2D point in Homogeneous coordinates has how many elements? |
|
||
| (2) | _____ |
A 2D rotation matrix in Cartesian coordinates has how many elements? |
|
\(\bs{T} = \left[ \begin{array}{r r} 0 & -1 \\ 1 & 0\end{array}\right] \)
\(\bs{S} = \left[ \begin{array}{r r r r} 0 & 1 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 1\end{array}\right] \)
\( \bs{R} = \left[ \begin{array}{r r} \cos \theta & -\sin \theta \\ \sin \theta & \cos \theta \end{array}\right] \)
and
\( \bs{S} = \left[ \begin{array}{r r} \alpha & 0 \\ 0 & \beta \end{array}\right] \)drawLine() method in the
Rasterizer2D class (that uses the classes/structs
from the programming assignments):
void Rasterizer2D::drawLine(const Matrix<2,1>& p, const Matrix<2,1>& q,
const Color& color)
{
double alpha, m;
if (q.get(0,0) == p.get(0,0))
m = INFINITY;
else
m = (q.get(1,0)-p.get(1,0))/(q.get(0,0)-p.get(0,0));
if ((m >= -1.0) && (m <= 1.0))
{
double y;
int xEnd, xStart;
if (p.get(0,0) <= q.get(0,0))
{
xStart = (int)round(p.get(0,0));
xEnd = (int)round(q.get(0,0));
}
else
{
xStart = (int)round(q.get(0,0));
xEnd = (int)round(p.get(0,0));
}
for (int x=xStart; x<=xEnd; x++)
{
if (q.get(0,0) == p.get(0,0))
{
y = p.get(1,0);
}
else
{
alpha = (x - p.get(0,0))/(q.get(0,0) - p.get(0,0));
y = p.get(1,0) + alpha * (q.get(1,0) - p.get(1,0));
}
fb->setPixel(x, (int)round(y), color);
}
}
else
{
double x;
int yEnd, yStart;
if (p.get(1,0) <= q.get(1,0))
{
yStart = (int)round(p.get(1,0));
yEnd = (int)round(q.get(1,0));
}
else
{
yStart = (int)round(q.get(1,0));
yEnd = (int)round(p.get(1,0));
}
for (int y=yStart; y<=yEnd; y++)
{
if (q.get(1,0) == p.get(1,0))
{
x = p.get(0,0);
}
else
{
alpha = (y - p.get(1,0))/(q.get(1,0) - p.get(1,0));
x = p.get(0,0) + alpha * (q.get(0,0) - p.get(0,0));
}
fb->setPixel((int)round(x), y, color);
}
}
}
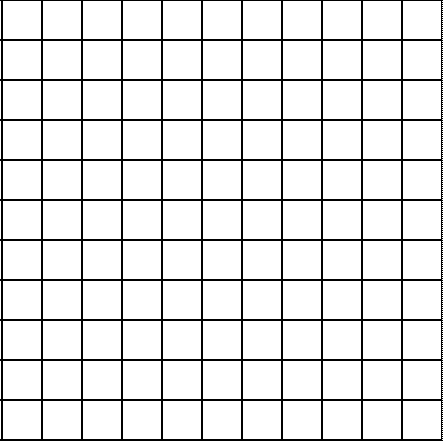
show (in the grid below) what will be drawn if this method is called as follows:
Color red = {255,0,0};
Matrix<2,1> p = { 0, 0};
Matrix<2,1> q = {10, 3};
rasterizer->drawLine(red, p, q);
You must assume that the lower-left pixel is the origin [i.e., (0,0)] and that the coordinates increase from left-to-right and bottom-to-top.
onLine() that is passed
a double containing the slope of the line,
a double containing the vertical intercept of the
line, and a Matrix<2,1> containing
a point. This function must return true
of the point is on the line and false otherwise.
sameSide() that is passed
two points defining a line and two test points. The method must
return true if the two points are on the same side
of the line and false otherwise.
sameSide() function above, write a function that
determines if a given point is inside a convex polygon.
Copyright 2014