|
|
Number[] n;
Integer[] i = new Integer[2];
i[0] = Integer.valueOf(0);
n = i;
n[1] = Double.valueOf(7.5);
Statistics class declared as follows:
public static int min(List<Comparable> data)
will the following fragment compile (assuming everything has been imported properly)? Explain.
List<Integer> data;
// Instantiate and initialize data
int m = Statistics.min(data);
ShapeLabel class that extends
JLabel
 and overrides its
and overrides its paint() method so that, instead of
rendering text, it renders the shape. The constructor must have a single
String parameter, and it must only accept
the String objects "Circle",
"Rectangle", "Square",
and "Triangle". It must also have a
setColor(Color c) method that can be used to set the
Color that the shape will be rendered in.
ShapeColorAction that can be used to set the
Color of a ShapeLabel (as described in an
earlier question). Your implementation must extend
AbstractAction
 ,
must have a
constructor that is passed the associated
,
must have a
constructor that is passed the associated ShapeLabel,
and must use a
JColorChooser
 . It
need not use a "background thread" (i.e.,
a
. It
need not use a "background thread" (i.e.,
a SwingWorker
 ).
).
IndexedGroup
abstract data type:
package collections;
/**
* The requirements of a group of elements that can be get/set
* using an integer index.
*/
public interface IndexedGroup<E>
{
/**
* Get the element at the given index
*
* @param index The index of interest
* @return The element at the given index
*/
public E get(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException;
/**
* Set the element at the given index. If the index does not yet
* exist, it will be created (space permitting). Some implementations
* may throw an IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is invalid.
*
* @param index The index of interest
* @param value The new value for the given index
*/
public void set(int index, E value);
}
complete the following FixedSizeIndexedGroup class:
package collections;
public class FixedSizeIndexedGroup<E> implements IndexedGroup<E>
{
Object[] values;
public FixedSizeIndexedGroup(int size)
{
values = new Object[size];
}
public E get(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
{
}
public void set(int index, E value) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
{
}
}
You may add private methods if you think they will improve your solution. Note: You may have to use some "unchecked or unsafe" operations.
Iterable
 interface.
To do so, you should create an
interface.
To do so, you should create an IndexedGroupIterator
class that implements
the Iterator
 interface. Note: The
interface. Note: The next() method should
return null elements that are in
the IndexedGroup.
IndexedGroupIterator class so that it also has
hasNextNonNull() and nextNonNull()
methods that behave as their names imply. Why are these methods
not likely to be used? (Hint: Think about the specification of the
Iterator interface.)
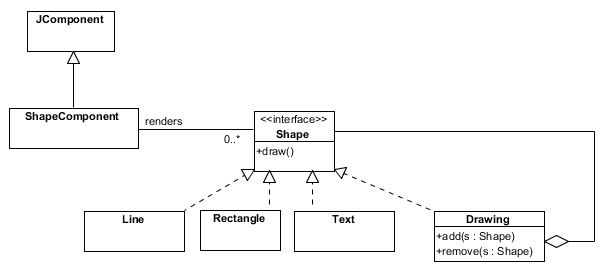
Shape
|
|
|
|
|
Line
|
|
|
|
|
Rectangle
|
|
|
|
|
Text
|
|
|
|
|
Drawing
|
|
|
|
|
operation()
|
|
|
|
|
Map object (e.g., a HashMap)
can contain only one value for each key. Hence, in order to
keep a mapping of, say, students to grades, one has to be creative.
One approach is to create
a ManyValuedMap class that does not provide all of the
functionality or a Map but delegates to an object
that implements Map. For example:
import java.util.*;
public class ManyValuedMap<K,V>
{
private HashMap<K,ArrayList<V>> delegate;
public ManyValuedMap()
{
delegate = new HashMap<K,ArrayList<V>>();
}
// Returns all of the values associated with a key (or null)
public ArrayList<V> get(K key)
// Adds the value to the ArrayList associated with the given key
public V put(K key, V value)
// Removes the value from the ArrayList associated with the given key
public V remove(K key)
}
Implement this class.
ManyValuedMap
above, one could extend the HashMap class as follows:
import java.util.*;
public class ManyValuedMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V>
{
// Searches through all of the values in all of the keys
public boolean containsValue(Object value)
// Returns the first value for this key
public V get(Object key)
// Returns all of the values associated with a key (or null)
public Iterator<V> getValues(K key)
// Adds the value to the ArrayList associated with the given key
public V put(K key, V value)
// Throws UnsupportedOperationException
public void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m)
// Removes the value from the ArrayList associated with the given key
public V remove(Object key)
// Returns a Collection of all of the values associated with all keys
public Collection<V> values()
}
Implement this class.
HashMap class as above,
one could decorate a Map as follows:
import java.util.*;
public class ManyValuedMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>
{
private Map<K,ArrayList<V>> decorated;
public ManyValuedMap(Map<K,ArrayList<V>> decorated)
{
this.decorated = decorated;
}
// All of the methods required in the Map interface should
// delegate to decorated as needed
// Returns all of the values associated with a key (or null)
public Iterator<V> getValues(K key)
{
Collection<V> values;
values = decorated.get(key);
if (values != null) return values.iterator();
else return null;
}
}
Implement this class.
ClintonTextField that replaces 'W' and 'w'
characters with spaces.
With that in mind, you must complete the
createDefaultModel() method in the
ClintonTextField below and the
insertString() method in the ClintonDocument
below.
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.text.*;
/**
* A JTextField that replaces 'W' and 'w' characters with spaces
*
*/
public class ClintonTextField extends JTextField
{
/**
* Construct a new ClintonTextField
*/
public ClintonTextField()
{
super();
}
/**
* Create a Document (i.e., model) for this ClintonTextField
*
* @return A ClintonDocument
*/
protected Document createDefaultModel()
{
}
}
import javax.swing.text.*;
/**
* A Document that replaces all 'W' and 'w' characters with
* spaces whenever a String is inserted into it.
*
*/
public class ClintonDocument extends PlainDocument
{
/**
* Inserts content into the document after replacing all 'W' and 'w'
* characters with space characters
*
* @param offs The starting offset
* @param str The string to insert
* @param a The attributes for the inserted text
*/
public void insertString(int offs, String str, AttributeSet a)
throws BadLocationException
{
}
}
CS446TextField:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
import javax.swing.text.*;
public class CS446TextField extends JPanel
implements DocumentListener
{
private JLabel label;
private JTextField textField;
private String txt;
/**
* Construct a new CS446TextField
*/
public CS446TextField()
{
super();
txt = new String();
label = new JLabel("I Love");
textField = new JTextField();
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add(label, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
add(textField, BorderLayout.CENTER);
textField.getDocument().addDocumentListener(this);
}
/**
* Handle insertUpdate events (required by DocumentListener)
*/
public void insertUpdate(DocumentEvent de)
{
label.setText(textField.getText());
}
/**
* Handle removeUpdate events (required by DocumentListener)
*/
public void removeUpdate(DocumentEvent de)
{
label.setText(textField.getText());
}
/**
* Handle changedUpdate events (required by DocumentListener)
*/
public void changedUpdate(DocumentEvent de)
{
}
}
CS446TextField look like immediately
after (i.e., before any keys are pressed)
it is added to a Container?
CS446TextField when it has the focus.
PulsingLabel class that
extends JLabel
 and uses
a
and uses
a Timer
 to
interatively increase the font size four times and then decrease
the font size four times (so that the text on the component
appears to "pulse".
to
interatively increase the font size four times and then decrease
the font size four times (so that the text on the component
appears to "pulse".
SwingWorker
 ).
Give a specific example
of what might "go wrong" otherwise.
).
Give a specific example
of what might "go wrong" otherwise.
JMUmble. In this system, arriving
messages are handled by a PostOffice
object. Depending on how the system is configured at runtime, one
or more objects might need to know when a message arrives. The
Department has currently implemented several such classes:
ScreenFlasher (which makes the entire screen flash --
you always know when a message has arrived),
PopularityTimer (which starts a clock that show the
amount of time since the most recent message arrived), and
Mumbler (which uses speech generation to read the name
of the person that sent the message -- this is where the system got
its name). Use the observer pattern to develop a class model of
this system (in UML). You do not need to include the attributes of
each class, only the operations/methods. Include comments that
describe each operation/method.
PrimeNumbersTask class.
public class PrimeNumbersTask extends SwingWorker<List<Integer>, Integer>
{
private ArrayList<Integer> primes;
private int current, numberOfPrimesToFind;
private JTextArea textArea;
public PrimeNumbersTask(JTextArea textArea, int numberOfPrimesToFind)
{
this.numberOfPrimesToFind = numberOfPrimesToFind;
this.textArea = textArea;
primes = new ArrayList<Integer>();
current = 2;
}
public List<Integer> doInBackground()
{
// TODO
}
private boolean isPrime(int n)
{
for (int i=2; i<n; i++)
{
if (n % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
private int nextPrimeNumber(int start)
{
for (int n=start+1; n<Integer.MAX_VALUE; n++)
{
if (isPrime(n)) return n;
}
return -1;
}
protected void process(List<Integer> chunks)
{
// TODO
}
}
Your implementation must satisfy the following specifications:
doInBackground() method must iterate until the desired
number of prime numbers has been found or until the task is cancelled.
doInBackground() method must return a List
containing all of the prime numebrs found.
JTextArea.
Copyright 2022