
log10(187) is in which of the following intervals,
\([0,1)\), \([1, 2)\), \([2, 3)\),
or \([3, 4)\)?
(int)log10(187)?
data.txt exists in the working directory
and contains the characters abcdefg)? Why?
int
main(void)
{
int fd;
fd = open("data.txt", O_RDONLY);
printf("%d\n", fd);
return 0;
}
data.txt exists in the working directory
and contains the characters abcdefg)? Why?
int
main(void)
{
char c;
int fda, fdb;
fda = open("data.txt", O_RDONLY);
fdb = open("data.txt", O_RDONLY);
read(fda, &c, 1);
printf("%c", c);
read(fdb, &c, 1);
printf("%c", c);
read(fda, &c, 1);
printf("%c", c);
return 0;
}
data.txt exists in the working directory
and contains the characters abcdefg)?
int
main(void)
{
char c;
int dupfd, fda, fdb;
fda = open("data.txt", O_RDONLY);
fdb = open("data.txt", O_RDONLY);
read(fdb, &c, 1);
printf("%c", c);
dupfd = dup(fda);
read(dupfd, &c, 1);
printf("%c", c);
dupfd = dup(fdb);
read(dupfd, &c, 1);
printf("%c", c);
read(fda, &c, 1);
printf("%c", c);
return 0;
}
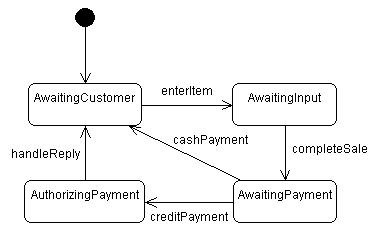
presentation (which can be opened
or closed) and the volume (which can be
1, 2 or 3).
opened state. Given this, draw the UML statemachine
diagram for this system.
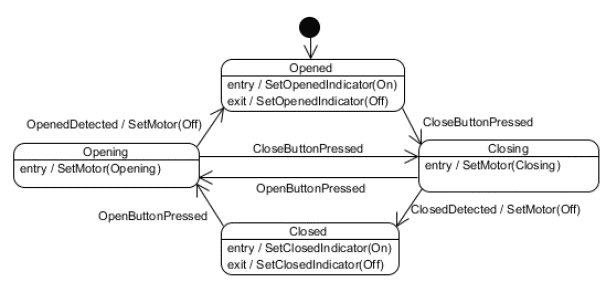
and the following files
hardware.h
#ifndef HARDWARE_H
#define HARDWARE_H
// LED Settings.
typedef enum
{
LED_OFF,
LED_ON,
LED_NUMBER_OF_SETTINGS
} led_setting;
// Motor Settings.
typedef enum
{
MOTOR_CLOSING,
MOTOR_OFF,
MOTOR_OPENING,
MOTOR_NUMBER_OF_SETTINGS
} motor_setting;
// Events.
typedef enum
{
CLOSE_BUTTON_PRESSED,
CLOSED_DETECTED,
OPEN_BUTTON_PRESSED,
OPENED_DETECTED,
NUMBER_OF_EVENTS
} event;
// Functions for controlling the LED Indicators.
void
set_closed_indicator(led_setting value);
void
set_opened_indicator(led_setting value);
// Functions for controlling the Motor.
void
set_motor(motor_setting value);
#endif
statemodel.h
#ifndef STATEMODEL_H #define STATEMODEL_H #include "hardware.h" #include "state.h" // Declare all of the states used in the state model. extern state closed; extern state closing; extern state opened; extern state opening; // Declare all of the global setup functions for the individual states. void setup_closed(); void setup_closing(); void setup_opened(); void setup_opening(); // Declare all of the functions used in the state model itself (i.e., // not in the individual states). void setup_states(); void handle_event(event current_event); #endif
state.h
#ifndef STATE_H
#define STATE_H
// Add an alias for a type to the global name space.
typedef struct state state;
// Add an alias for event handlers.
typedef state* event_handler(void);
// Add an alias for actions.
typedef void action(void);
// Define the identifier state as a struct.
struct state {
event_handler* close_button_pressed;
event_handler* closed_detected;
event_handler* open_button_pressed;
event_handler* opened_detected;
action* entry_to;
action* exit_from;
};
// Declare variables to hold pointers to the default event handler and
// the default action.
extern event_handler* default_event_handler;
extern action* default_action;
// Declare a variable to hold the default state.
extern struct state default_state;
#endif
state.c
#include "state.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
// Define all of the functions that are not exposed
// by the header file.
state*
return_null()
{
return NULL;
}
void
return_void()
{
}
// Define the default event handler and default action
event_handler* default_event_handler = return_null;
action* default_action = return_void;
// Define the default state
struct state default_state = {
return_null, // close_button_pressed
return_null, // closed_detected
return_null, // open_button_pressed
return_null, // opened_detected
return_void, // entry_to
return_void // exit_from
};
complete the files opening.h and opening.c
below. You may assume that the
function setup_opening() will be called before any
other functions in opening.c are.
All functions and variables must have appropriate linkage and scope.
opening.h
#ifndef OPENING_H #define OPENING_H #include "state.h" // Declare all of the functions performed when in the opening state. // Define (tentatively) the opening state (and initialize it to the // default state). #endif
opening.c
#include "opening.h" #include "hardware.h" #include "statemodel.h" // For the other states // Define the setup_opening() function. // Define all of the functions performed when in the opening state.
printf() calls
in the following program:
#include <stdio.h>
int
main(void)
{
int i;
int j;
int *p;
int *q;
i = 5;
printf("i: %d\n", i);
printf("&i: %d\n", &i);
j = 9;
printf("j: %d\n", j);
printf("&j: %d\n", &j);
p = &i;
printf("p: %d\n", p);
printf("*p: %d\n", *p);
j = i;
q = &j;
*q = 7;
printf("i: %d\n", i);
printf("j: %d\n", j);
printf("q: %d\n", q);
printf("*q: %d\n", *q);
*p = *q;
j = 3;
printf("i: %d\n", i);
printf("j: %d\n", j);
printf("*p: %d\n", *p);
}
is as follows:
i: 5 &i: 2686736 j: 9 &j: 2686740
what will be printed by the remaining printf() calls?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char eid[9]; // 8 characters plus '\0'
int grade;
int
main(void)
{
// Addresses (in the data segment)
printf("eid is at %p\n", eid);
printf("eid[9]is at %p\n", &eid[9]);
printf("grade is at %p\n", &grade);
// Initialization
strcpy(eid, "bernstdh");
grade = 100;
// Output after initialization
printf("Grade for %s: %d\n", eid, grade);
// A defect
strcpy(eid, "bernstdh ");
// Output after the defect
printf("Grade for %s: %d\n", eid, grade);
}
int
main(void)
{
int status;
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
switch(pid)
{
case 0:
printf("c");
break;
default:
printf("p");
break;
}
}
int
main(void)
{
int status;
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
switch(pid)
{
case 0:
printf("c");
break;
default:
wait(&status);
printf("p");
break;
}
printf("b");
}
int
main(void)
{
int status;
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
switch(pid)
{
case 0:
printf("a");
break;
default:
printf("b");
break;
}
pid = fork();
switch(pid)
{
case 0:
printf("c");
break;
default:
printf("d");
break;
}
printf("e");
}
How many characters will be output?
data.txt exists in the working directory and
contains the characters abcdefg.
int
main(void)
{
char c;
int fd, status;
fd = open("data.txt", O_RDONLY);
if (fork() == 0)
{
read(fd, &c, 1);
exit(0);
}
wait(&status);
read(fd, &c, 1);
printf("%c", c);
return 0;
}
wait() is removed from the above program.
What will be printed? Note: If there are multiple possibilities, list them
all.
int
main(void)
{
execl("/bin/date", date, NULL);
printf("Are you late?\n");
}
execl().
execl() is executed.
"The current date and time are\n".
After the child process terminates, the parent process must execute
the program named /bin/date.
"The current date and time are\n". After the first
child process terminates, the second child process must execute the
program named /bin/date. After the second child process
terminates, the parent process must print the string
"Are you late?\n"
Copyright 2017