

Purpose: HeinousAlienLocator is a class that can be used to locate an alien if it is on the JMU campus.
and uses the following image:
You will only use the Sensor class directly (the
Sensor class uses the SensorDisplay class).
Further, you will only use the int scan(int x, int y, int width)
method in this class. This method is passed the square area
to scan (x and y are the upper-left corner
of the area and width is the width and height of the square).
It returns -width if the alien is not in the square area and
width if the alien is in the square area.
When running, the Sensor looks something like the following:
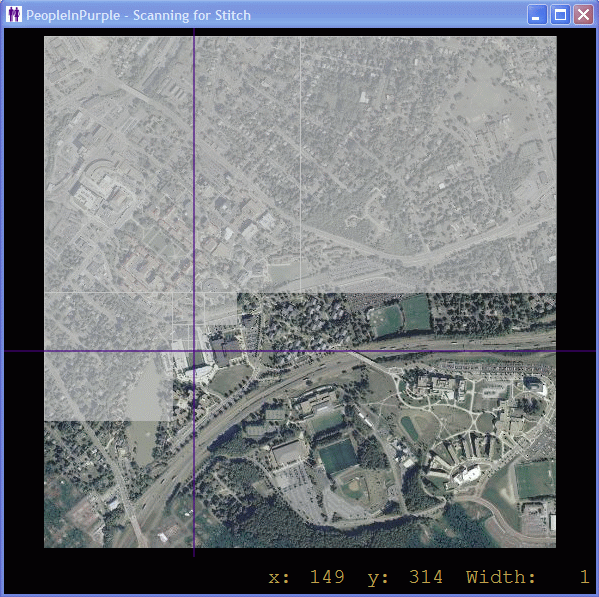
The gray areas are those that did not contain the alien of interest, the purple lines are used to delineate the area that is currently being scanned, and the flashing purple square (not shown) indicates the area that is currently being scanned.
HeinousAlienLocator class with the following
public methods:
import java.awt.Point;
public class HeinousAlienLocator
{
public HeinousAlienLocator(Sensor sensor)
{
// Your code here
}
public Point search(int x, int y, int width)
{
// Your code here
}
// Your code here
}
The search() method
will be called by the HALDriver to initiate a
search in the area defined by the parameters x,
y, and width. Hence, the
search() method is responsible for doing the work of
locating the alien (thought it can, of course, call other methods).
This method must return null if the alien is not in the
area of interest and must return a Point object
with the coordinates of the cell containing the alien if it is
in the area of interest.
Your implementation must satisfy the Software Requirements Specification (SRS).
You must use the following driver to test your code (and you must not change it):
HALDriver ( Source Code )
Command-line argument 0 contains the name of the alien to search for (and is required), command-line argument 1 contains the number of milliseconds to devote to each scan (and is optional).
Note that the driver does three main things: constructs a Sensor
object, constructs a HeinousAlienLocator object (passing
the constructor the Sensor to use), and calls the
HeinousAlienLocator object's search() method
passing it the square that contains the entire campus.
For debugging purposes:
HeinousAlienLocator is doing.
Scanner window with a scan time of 0.
The first thing to think about is how to define the "easy/base" case. To
do so, suppose your HeinousAlienLocator calls
the scan() method in the Sensor class.
When is its job really easy? (Hint: There may be more than one easy case.)
The second thing to think about is what you need to do to refine other cases (i.e., take hard cases and move them closer to the easy case).
Copyright 2011